In compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation ( GDPR ), national agencies could or may issue penalties for serious data privacy breaches. In conjunction of or irrespective of any measures or disciplinary laws, the penalties are imposed, including the requirement of cancel a breach, an injunction to change the data analysis to conform with the GDPR, and also the authority to enforce a provisional or permanent restriction or perhaps a data acquisition prohibition. He could be liable to sanctions explicitly in combination with the regulator for the requirements which apply to processors.
In this article, we will break down the GDPR, which deals with non-compliance fines. It would also give some good guidelines of GDPR offenses that can be easily overlooked but fortunately easily resolved and remedied as well.
What is GDPR in general?

The GDPR means “general data protection regulation.” It’s a complex series of laws that effectively reinforce data security policies for any company dealing with data from EU citizens. Plus, it offers the same people a whole range of new powers over their records, particularly if on the computer of a distant corporation servers.
We have listed a summary below:
- No enterprise throughout the EU or anywhere else can collect EU resident’s personal details before even obtaining direct, unquestionable, freely granted consent. It involves the vague data obtained by client cookies.
- EU consumers will have convenient access on sensitive details to check, modify, or erase the details. Upon requesting a full encrypted copy of an individual’s data must be given.
- Personal data privacy and encryption will be incorporated into the whole architecture of a website, including a smartphone device. Also, privacy by design is already required.
- The privacy policy can be presented in concise, transparent terms and rendered available to consumers. In some sense of openness, improvements to privacy management procedures and data violations need to be immediately reported to their clients.
This will apply to :
Since the law would not only refer to EU citizen’s personal details, the GDPR would be applied to any company that gathers the information around the globe.
Why we need GDPR

The reason behind the demand for adherence with the GDPR boils down to something like the one principle that no commercial deal will ever actually occur without it: confidence.
The GDPR attempts to ensure, consumers will rely on organizations for the privacy of their personal data to preserve consistency in respect to the information they use and to warn consumers of the infringement in a reasonable time, mostly in case of a security breach.
Fines for GDPR
Companies are liable for GDPR infraction in 2 levels;
- Infringements at the lesser magnitude can be subject to penalties at 10 million dollars or 2 % or more than the violator ‘s worldwide taxable profits. Such as profit before expense.
- A much more serious breach could lead to 20 million euros or to 4% of the annual income of the infringer – whichever is greater again. People can also be fined for GDPR breaches by using the identity data of many other parties, even for a reason other than financial.
Examples of GDPR Violations
Noncompliant Consent Methods
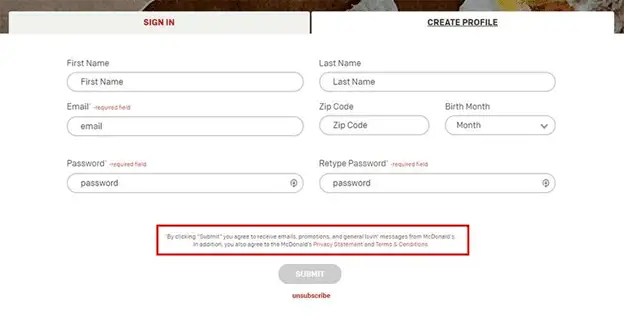
Some of the main aspects of GDPR implementation is legitimate consent. It’s not easy to spot breaches. The login process for McDonald’s doesn’t really require individuals to donate their direct and explicit permission to marketing messages, so this would allow a user to apply for a profile.
Readability and Accessibility
Another fineable breach includes straightforward, so easy to comprehend rules on privacy. That long-winded, misleading legal jargon, which was so common in previous privacy agreements, won’t be tolerated anymore. Below is an Intro definition of a penalizable business. The terminology is highly nuanced and thick. While it is still ambiguous how severe these types of infringements will be, it’s indeed wise to ensure that a company’s Privacy Policy was clearly written in plain language.

Conclusion
The examples above illustrate a variety of infringements, including warnings to fines, which can result in a number of different punishments. If a blend of infringements is found, or when a corporation commits repeated offences, the bigger fines can begin to push in.
Ensure that the user agreement is current and updated regularly as well as contains GDPR required data, is written clearly and easy to comprehend. It should also get a fitted level of consent if collecting personal information. Have these in line with all your privacy and security practices so you can prevent violations.